Clinical Research
Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration | Diabetic Macular Edema | Retinal Vein Occlusion
Discover how RetInSight’s AI-powered Fluid Monitor can revolutionize your clinical studies by going beyond traditional markers like Central Subfield Thickness (CST).
While CST has long been used as a surrogate marker for disease activity, research shows a low correlation between changes in visual acuity (VA) and changes in CST after anti-VEGF therapy.1 These findings suggest that CST alone is not a reliable guide for personalized treatment decisions, emphasizing the need for more precise biomarkers.2

Why fluid biomarkers matter in clinical studies
Fluid biomarkers such as Intraretinal Fluid (IRF), Subretinal Fluid (SRF), and Pigment Epithelial Detachment (PED) provide a deeper understanding of disease progression and treatment efficacy, particularly in exudative macular diseases like nAMD, DME, and RVO.
Our advanced AI-based tools allow for the automated detection and quantification of fluid volumes within each retinal layer at ultra-structural level, providing a detailed, compartment-specific analysiis.3 These fluid biomarkers are now recognized as critical indicators for assessing treatment outcomes, enabling a new level of precision in personalized care.
Key features of the RetInSight Fluid Monitor in clinical studies
- Automated segmentation: Real-time analysis of fluid volumes helps researchers and clinicians avoid mistreatment and make informed decisions immediately.
- Compartment-specific analysis3: Each fluid compartment (IRF, SRF, PED) reveals unique response patterns, facilitating a more personalized approach to treatment.
- Retrospective analysis: Utilize OCT images to perform a retrospective assessment, enabling correlation between fluid volumes and visual acuity over time.
Impact of fluid biomarkers on treatment outcomes
Different fluid compartments impact treatment needs and visual outcomes differently:
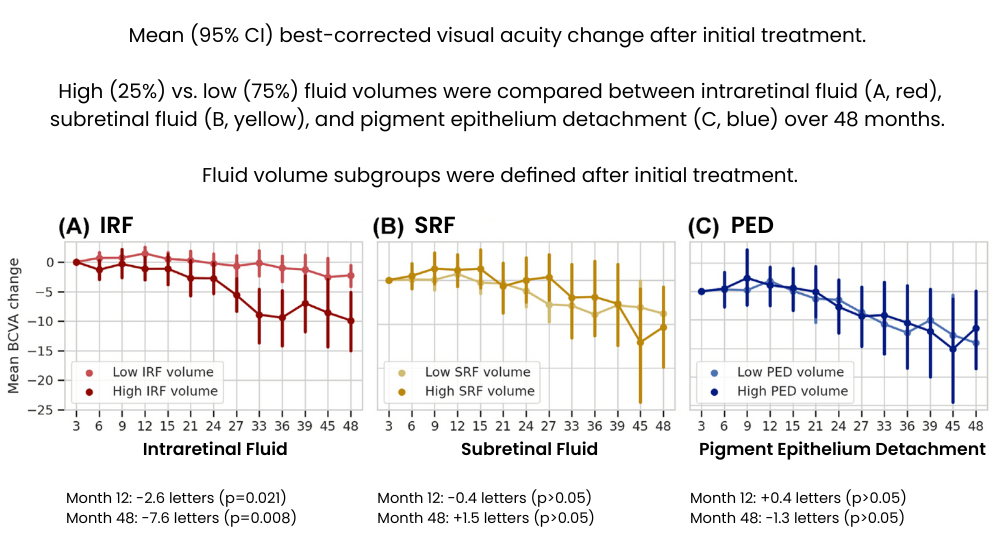
Intraretinal Fluid (IRF)4
- High IRF volumes after initial treatment are associated with significant vision loss at both 12 months (-2.6 letters) and 48 months (-7.6 letters).
- Patients with elevated IRF levels required an average of 1.6 more treatments at 12 months and 5.3 more treatments at 48 months compared to those with lower IRF volumes.
Subretinal Fluid (SRF) and Pigment Epithelial Detachment (PED)4
- While SRF and PED do not independently result in significant vision loss, their presence correlates with increased disease activity.
- Higher volumes of SRF and PED necessitate more frequent anti-VEGF treatments to maintain stable visual outcomes.
Benefits of using the RetInSight Fluid Monitor in your clinical study
- Comprehensive reporting: All key fluid parameters – IRF, SRF, PED, and CST – are displayed in a single report, making it easy for study monitors and auditors to review data.
- Real-time decision-making: Immediate feedback based on fluid volume changes ensures accurate treatment decisions.
- Visual assessment: En-face images enable visual scan checks.
- User-friendly integration: Easy upload process with no special equipment required; compatible with any web browser.
- Enhanced patient communication: Detailed reports facilitate patient communication, supporting patient retention.
- Secure data management: All reports are securely stored within the system and can be accessed or reprinted at any time, ensuring compliance with data security protocols.
Interested in understanding the impact of fluid biomarkers?
Discover how fluid biomarkers can enhance the understanding of your therapy’s efficacy and substantiate your data package.
References
- Neil M. Bressler et al. | Association Between Change in Visual Acuity and Change in Central Subfield Thickness During Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema in Participants Randomized to Aflibercept, Bevacizumab, or Ranibizumab
- Maximilian Pawloff et al. | Systematic correlation of central subfield thickness (CSFT) with retinal fluid volumes quantified by deep learning in the major exudative macular diseases
- Schmidt-Erfurth Ursula et al. | Application of Automated Quantification of Fluid Volumes to Anti-VEGF Therapy of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- Gregor S. Reiter et al. | Long-term effect of fluid volumes during the maintenance phase in neovascular age-related macular degeneration in the real world: results from Fight Retinal Blindness!